Aluminum extrusion process
The aluminum alloy extrusion process actually begins with the product design, because the product design is based on the given usage requirements, which determine many final parameters of the product.Such as the product's mechanical processing performance, surface treatment performance and the use of environmental requirements, these properties and requirements actually determine the choice of extruded aluminum alloy.
However, the properties of extruded aluminum are determined by the design shape of the product.The shape of the product determines the shape of the extrusion die.
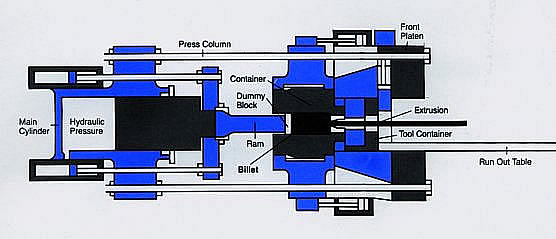
Once solved the design problem, the practical extrusion process is starting extrusion cast in aluminum rod, aluminum casting rod must be heated before extrusion to soften it, the heating good aluminum casting rods sheng ingot is put in the extruder barrel inside, and then by high power hydraulic cylinder pushing extrusion rod, the front end of the extrusion rod has a pressure pad, such heated soft aluminum alloy in dummy block under strong pressure from mold precision molding extrusion molding.
This is what a mold is for: the shape of the product needed for production.
The picture is: typical horizontal hydraulic extruder schematic diagram
The direction of extrusion is left to right
This is a simple description of the most widely used direct extrusion today. Indirect extrusion is a similar process, but there are some very important differences.
In the indirect extrusion process.The die is installed on the hollow extrusion bar, so that the die is pressed towards the immovable aluminum bar blank, forcing the aluminum alloy to extrude towards the hollow extrusion bar through the die.
In fact, the extrusion process is similar to squeezing the toothpaste. When the pressure is applied to the closed end of the toothpaste, the cylindrical toothpaste is squeezed through the circular opening.
If the opening is flat, the squeezed toothpaste comes out as a ribbon.
Of course, complex shapes can also be squeezed out at openings of the same shape.For example, cake makers use specially shaped tubes to squeeze ice cream to make all kinds of frills.
While you can't make many useful products with toothpaste or ice cream, you can't squeeze aluminum into tubes with your fingers.
But you can use a powerful hydraulic press to extrude aluminum from a given shape of mold to produce a wide variety of useful products of almost any shape.
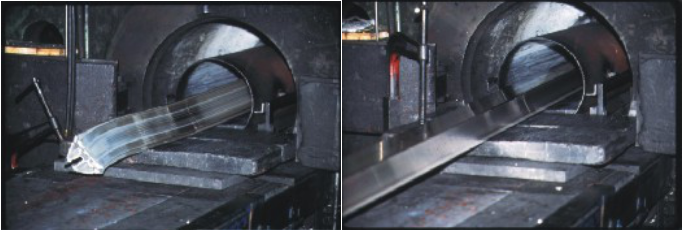
The figure below (left) shows the first section of the extruder at the beginning of extrusion. (right)
The bar
The aluminum bar is the blank of the extrusion process. The aluminum bar used for extrusion can be solid or hollow, usually cylindrical, and its length is determined by the extrusion tube.
Aluminum rods are usually formed by casting, or by forging or powder forging.It is usually made by sawing aluminum alloy bars with good alloy composition.
Aluminum alloys are usually made up of more than one metal element. Extruded aluminum alloys are made up of trace (usually no more than 5%) elements (such as copper, magnesium, silicon, manganese, or zinc) that improve the properties of pure aluminum and affect the extrusion process.
The length of aluminum rod varies from manufacturer to manufacturer, which is determined by the final required length, extrusion ratio, discharge length and extrusion allowance.
Standard lengths generally range from 26 inches (660mm) to 72 inches (1830mm). Outside diameters range from 3 inches (76mm) to 33 inches (838mm), 6 inches (155 mm) to 9 inches (228 mm).
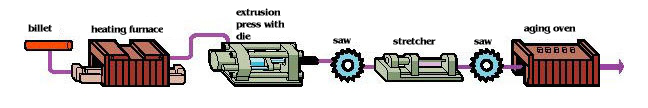
Direct extrusion process
[billet] [heating furnance] [extrusion press with die] saw [strecher] [aging overn]
The diagram illustrates the basic steps of extruding an aluminum bar
When the final product shape is determined, the appropriate aluminum alloy is selected, the extrusion die manufacturing is completed, and the preparation for the actual extrusion process is completed.
Then preheat the aluminum bar and the extrusion tool. During the extrusion process, the aluminum bar is solid, but has softened in the furnace.
The melting point of aluminum alloy is about 660℃.The typical heating temperature of the extrusion process is generally greater than 375℃ and can be as high as 500℃, depending on the extrusion condition of the metal.
The actual extrusion process begins when the extrusion rod begins to apply pressure to the aluminum rod in the ingot.
Different hydraulic presses are designed to squeeze anywhere from 100 tons to 15,000 tons.This extrusion pressure determines the size of the extrusion produced by the extrusion machine.
Extruded product specifications are indicated by the maximum cross section size of the product, sometimes also by the circumferential diameter of the product.
When the extrusion has just begun, the aluminum bar is subjected to the reaction force of the mold and becomes shorter and thicker, until the expansion of the aluminum bar is restricted by the ingot barrel wall;
Then, as the pressure continues to increase, the soft (still solid) metal has no place to flow and starts to be squeezed out of the mold's forming hole to the other end of the mold, forming the profile.
About 10% of the aluminum rod (including the aluminum rod skin) is left in the ingot barrel, the extrusion product is cut from the mold, and the remaining metal in the ingot barrel is cleaned and recycled.After the product leaves the mold, the subsequent process is that the hot extrusion product is quenched, machined and aged.
When the heated aluminum is extruded from the mold through the ingot cylinder, the metal in the center of the aluminum bar flows faster than the edge.As the black stripe in the illustration shows, the metal around the edges is left behind to be recycled as a remnant.
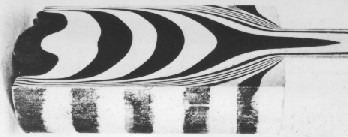
The rate of extrusion depends on the alloy being squeezed and the shape of the die outlet hole. Using hard alloy to squeeze complex shaped materials can be as slow as 1-2 feet per minute.With soft alloys, simple shapes can be squeezed to 180 feet per minute or more.
The length of the extrusion product depends on the aluminum bar and the mold outlet hole. A continuous extrusion can produce a product up to 200 feet long.The latest molding extrusion, when the extruded product leaves the extruder is placed on the slide (equivalent to the conveyor belt);
According to the different alloy, the extrusion out of the product cooling mode: divided into natural cooling, air or water cooling but quenching.This is a key step to ensure the metallographic performance of the product after aging.The extruded product is then transferred to a cold bed.
Straighten
After quenching (cooling), the extruded product is straightened and straightened by a stretcher or straightener (stretching is also classified as cold working after extrusion).At last, the product is transferred to the sawing machine by the conveying device.
Sawing
Typical finished product sawing is the sawing of a product to a specific commercial length.Circular saws are the most widely used today, like rotary arm saws that cut long pieces of extruded material vertically.
There are also saws cut from the top of the profile (such as electric miter saw).Also useful saw table, saw table is with a disc saw blade from the bottom up to cut the product, and then the saw blade back to the bottom of the table for the next cycle.
A typical finished circular saw is 16-20 inches in diameter and has more than 100 carbide teeth.Large saw blades are used for large diameter extruders.
The self-lubricating sawing machine is equipped with a system that delivers lubricant to the sawtooth to ensure optimum sawing efficiency and the surface of the saw.
An automatic press holds the sections in place for sawing and the sawing debris is collected for recycling.
Ageing:
Some extruded products require aging to achieve optimum strength, so it is also called aging.Natural aging is performed at room temperature.Artificial aging is carried out in the aging furnace.Technically, it is called precipitation intensive phase heat treatment.
When the profile is extruded from the extruder, the profile becomes semi-solid.But it soon becomes solid when it is cooled or quenched (whether air-cooled or water-cooled).
Non-heat treated aluminum alloys (such as aluminum alloys with added magnesium or manganese) are strengthened by natural aging and cold working.Heat treatable aluminum alloy (such as aluminum alloy with copper, zinc, magnesium + silicon) can obtain better strength and hardness by affecting the heat treatment of the alloy metallographic structure.
In addition, aging is to make the particles of the strengthened phase evenly separated to obtain the maximum yield strength, hardness and elasticity of the special alloy.
Bales
Whether aging furnace or room temperature aging, after full aging, the profile is transferred to the surface treatment or deep processing workshop or bales ready for transport to the customer.
People also ask
Post time: Mar-20-2020